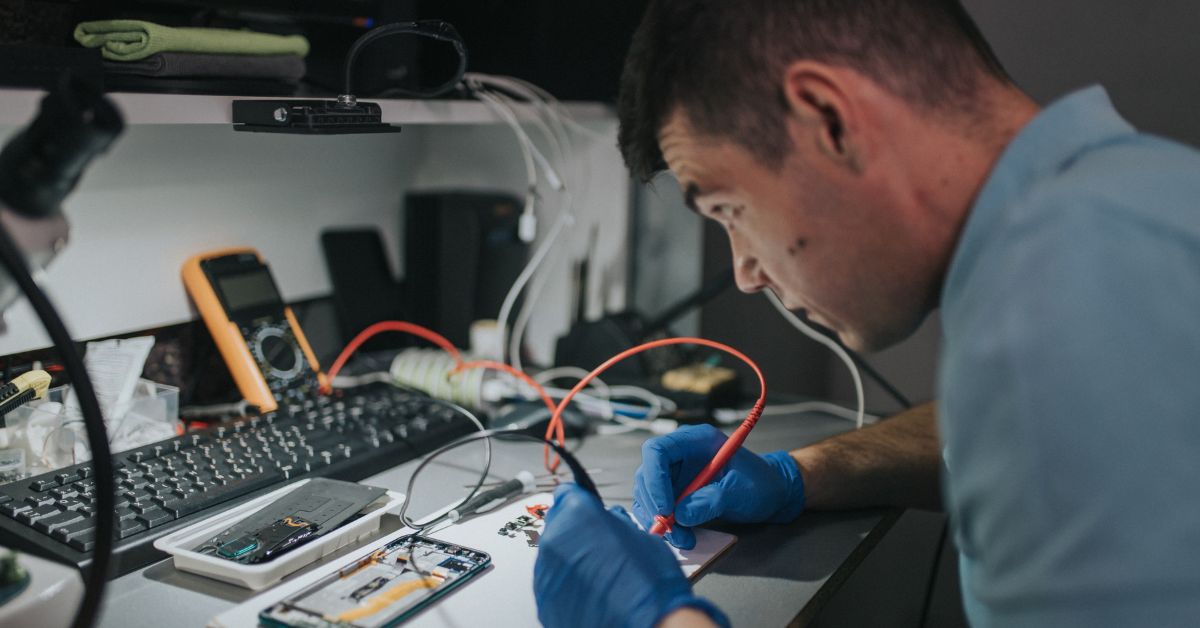
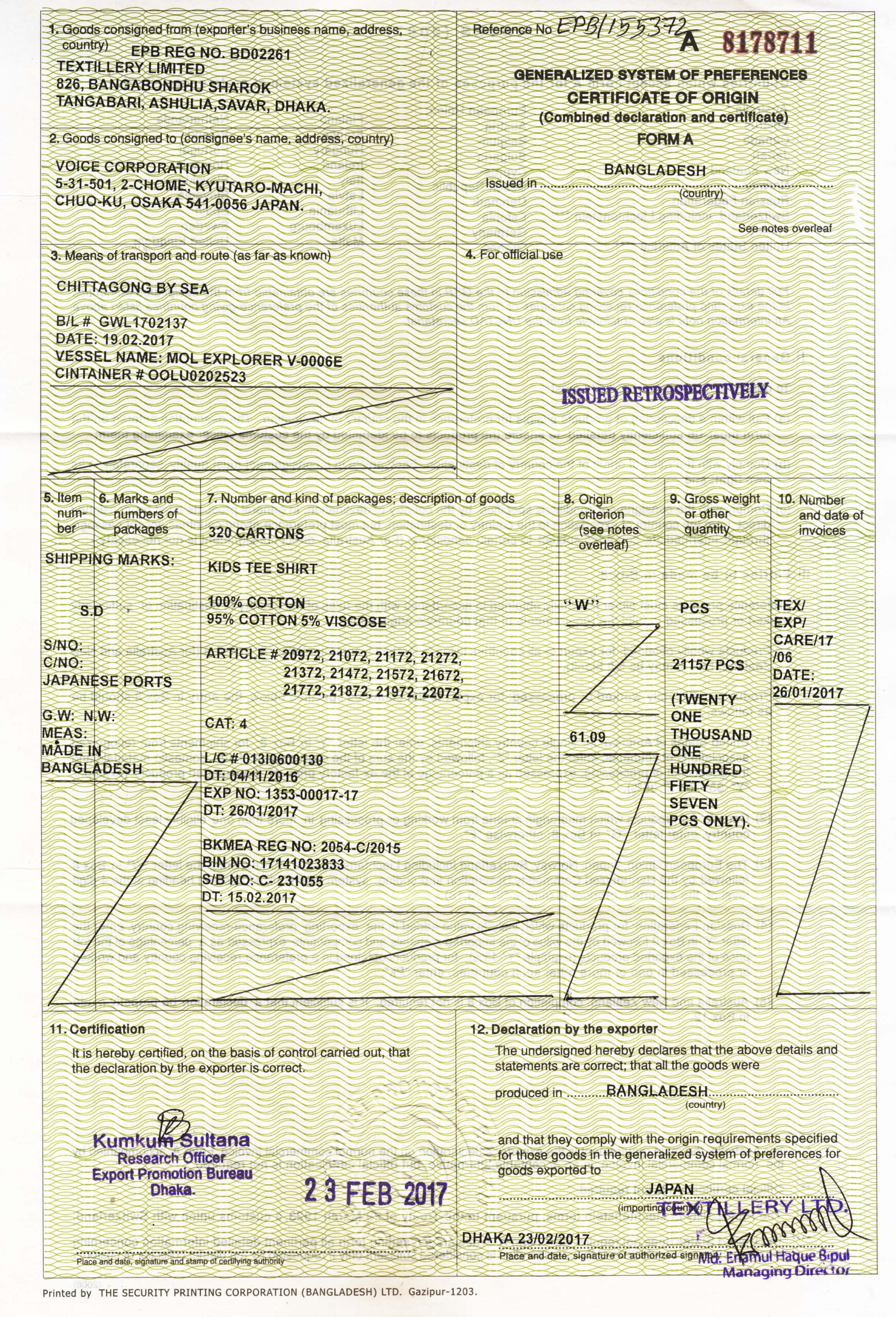
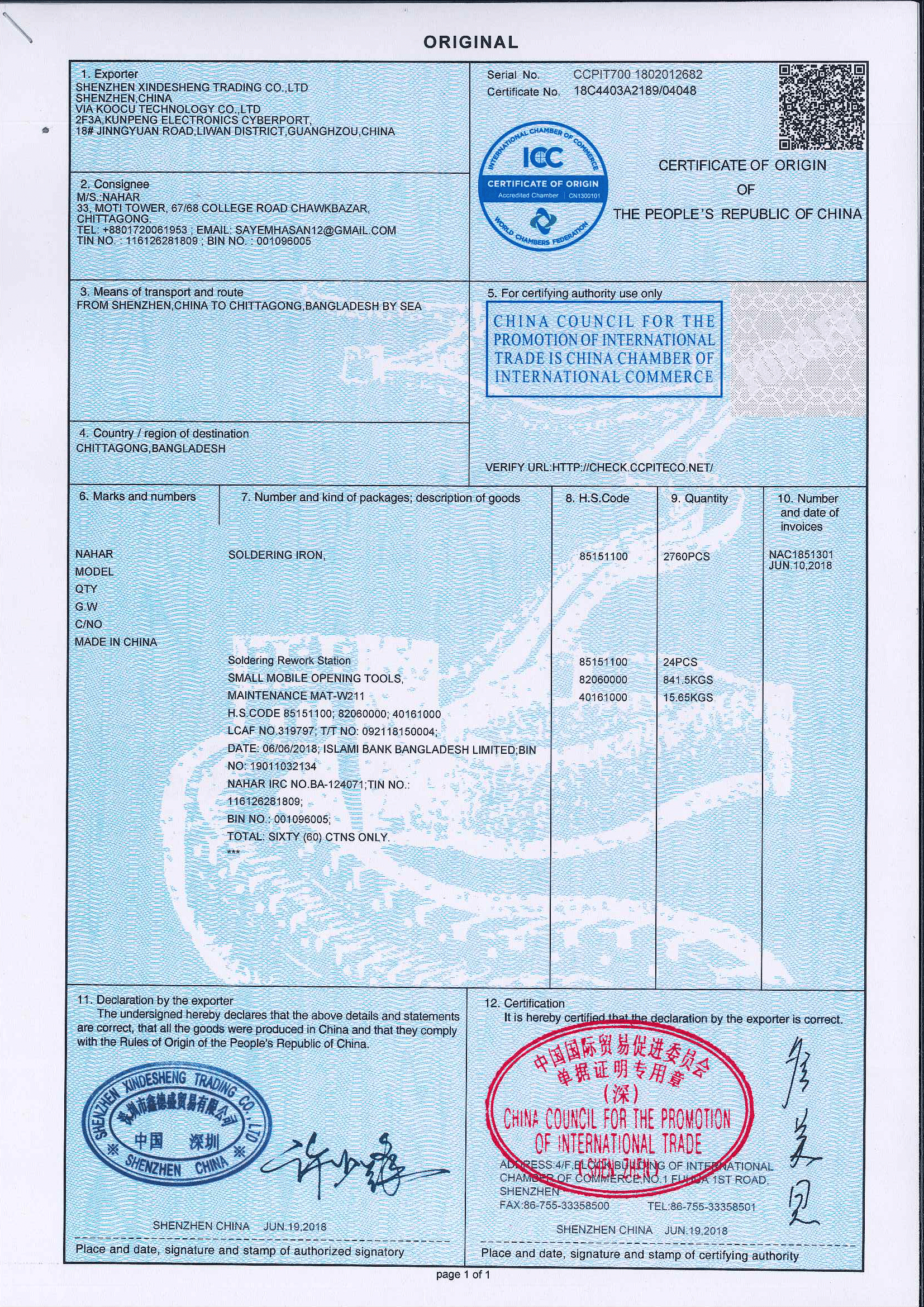
Why will you invest in importing mobile repairing tools and open a mobile repairing or servicing shop?
You can actually open the whole store with an investment of around $300 only and start the business. The machines, tools, materials and equipment that you need are not at all high prices and pretty cheap and easy to import if you want to import by yourself from China or any other country. At the end of the day you will have a high profit margin with very low investment.
In this blog I will tell you from my own experience in this mobile repairing or mobile servicing shop business the A to Z details you need to open the shop. This blog will be with all the information with a complete solution of opening a mobile repairing or mobile servicing shop and the machines, tools and mobile parts that you can import from China.
Table of Contents
- Increasing Demand of Mobile
- Steps to Open a Business of Mobile Repairing or Mobile Servicing Shop
- Step 01: You need to learn the skills to repair
- Step 02: Rent a Small Shop in a Good Location
- Step 03: Buy Different Tools from the Local Market or Import those Tools
- Step 04: Materials you Need to Repair Mobile Phones
- Step 05: Equipment that is needed to repair mobile phones
- Step 06: Some of the Parts of a Mobile Phone
Increasing Demand of Mobile
So we see the mobile demand has increased many fold at present times with pandemic increasing the demand to a high extent. You see, you need to have a mobile now for all the activities, starting from studies, shopping, playing, watching entertainment. You name it and you need the mobile. So more mobile means more mobile will have technical problems and shut downs and need repairing but we can see the shortages of mobile technicians and more repairing shops. I can see in my shop many customers are waiting now more than before to repair their mobiles.
Steps to Open a Business of Mobile Repairing or Mobile Servicing Shop
So now you have an opportunity in hand to open a business in a mobile repairing or mobile servicing shop. You have decided your objective. So now the steps start.
Step 01: You need to learn the skills to repair
You need to learn the skills to repair. You can enroll in a practical course in your locality or learn from the person who is in the business of mobile phone repairing or servicing. For me, I learned from an instructor who takes the course in 4 months. Actually 4 months or 6 months training is ok for you to get the basics complete. After that you can work on your own to develop your skills. As you know, there are different types of mobile in the market. The basics are the same for all the mobiles. You will have a PCB (printed circuit boards) and all the components are connected around it. So in summary, Learning the trade is important and developing the skills. This technical know-how is very important to start a mobile repairing or mobile servicing shop.
Step 02: Rent a Small Shop in a Good Location
The space of the shop need not be big as you do not need a big space to run the business. The shop can be in a good location where you will be seen by many people. This is important because you are providing a service and people have to know where your location is. At present, you can also make your shop be promoted in facebook pages and other social media to promote your shop. You can also do “ Google My Business “ which is an easy-to-use tool for businesses and organizations to manage their online presence across Google, including Search and Maps. To help customers find your business, and to tell them your story, you can verify your business and edit your business information.
Step 03: Buy Different Tools from the Local Market or Import those Tools
- Screw drivers, you need to have a range of small drives. Precision Screwdriver T4, T5, T6, and T7 are mostly needed. Screwdrivers to open the mobile phone like T4 screwdriver, most mobiles at present are opened by this screwdriver. To open a Nokia phone u need mostly T6, To open Iphone you need T3 and with that supporting other screwdrivers.
- Need tweezers to hold very small parts, Tweezers are small hand tools used for grasping objects too small to be easily handled with the human fingers. Tweezers are thumb-driven forceps most likely derived from tongs used to grab or hold hot objects.
- To open the casing of the mobile you need 2 types of mobile phone opener.
- Scissors to cut wires and other things, this is a thing you will need a lot for every other purpose.
- To clean everything including the motherboard of the mobile you need a brush.
Step 04: Materials you Need to Repair Mobile Phones
- Soldering Wire to connect all the circuits of the motherboard. Solder wires are generally two different types – lead alloy solder wire and lead-free solder.
- To melt the soldering wire with heat you need soldering paste or rosin.
- Solder paste is commonly used to create electrical connections and mechanical bonds between printed circuit board pads and surface mount devices, such as resistors and capacitors. It is made up of powdered solder in a flux paste.
- To join one assembly to another assembly u need jumping wire. A jump wire (also known as jumper, jumper wire, DuPont wire) is an electrical wire, or group of them in a cable, with a connector or pin at each end (or sometimes without them – simply “tinned”), which is normally used to interconnect the components.
- To remove excess soldering in the circuit you need desoldering wire. Desoldering braid or desoldering wick is a pre-fluxed copper braid that is used to remove solder allowing components to be replaced and excess solder (e.g., bridging) to be removed.
- To stop high heat to fall in Circuit board from the hot gun, use a heat protector tape. Heat protector tape is very important to protect the circuit boards and other heat sensitive components of the mobile circuit.
- To repair the display and to attach the battery to the motherboard we use a double tap with both sides glued and sticked.
- To prevent jumper wire to connect in different circuit use paper tape
- To hold the display and motherboard need adhesive glue. Adhesive, any substance that is capable of holding materials together in a functional manner by surface attachment that resists separation. “Adhesive” as a general term includes cement, mucilage, glue, and paste—terms that are often used interchangeably for any organic material that forms an adhesive bond.
Step 05: Equipment that is needed to repair mobile phones
- Soldering Iron to work on the motherboard. A soldering iron supplies the heat that melts the solder. It consists of a tip, which you apply to the metal parts you want to solder together, and an insulated handle so that you can hold the iron.
- A Meter or multimeter for current. A multimeter is a measuring instrument that can measure multiple electrical properties. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, resistance, and current, in which case it is also known as a volt-ohm-milliammeter (VOM), as the unit is equipped with voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter functionality.
- DC power supply. A DC power supply provides direct current (DC) voltage to power a device under test such as a circuit board or electronic product. A DC power supply typically sits on an engineer’s work area or bench and is often referred to as a bench power supply.
- Hot Air Gun to remove the SMD in motherboard or replace or take out: A Hot Air Gun is needed to blow hot air in the circuit in the SMD to remove them or replace them.
- What is SMD? SMD means surface mounted devices. SMD is a term used for all the components that don’t have pins going to the other side of the PCB, but have their electrical connections on the edges like the resistors, bios, audios and sata chips, as well as the chip set itself.
- Battery booster to recharge the voltage of the battery. A portable battery, fitted with cables and a charger, used to charge a dead battery.
- Display separator to separate display and the touch of the smartphone.
- Gum remover to remove the gum from the display and the touch of the smartphone
- Digital microscope or mini microscope to see the small SMD of the latest smartphones
- PCB stand: This is used to hold the PCB
- Thinner: To clean the PCB.
- Blade Cutter: A blade is the portion of a tool, weapon, or machine with an edge that is designed to puncture, chop, slice or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are to be used on.
- Ultrasonic Cleaner: To clean PCB and electronic components.
- BGA Kit: To reball and repair ball type IC
- Magnifying lens: Magnifying glasses are a simple optical device used for viewing details of objects with some magnification. To get a magnified view of PCB and other small mobile components.
- Cleaning Sponge: To clean the tip of the soldering iron.
Step 06: Some of the Parts of a Mobile Phone
- Touch Screen: A touch screen is any display that you interact with by touching it. A touchscreen works by having the top of the display that you touch come in contact with an electrically conductive layer underneath it. That layer below always has an electrical current running through it. When the two layers touch, the stream changes and registers your touch.
- Ringer of a mobile phone: The ringer alerts the user to an incoming call by emitting an audible tone or ring. Ringers are of two types, mechanical or electronic.
- Speaker of the mobile phone: The speaker is typically located at the bottom of the phone to the right of where you plug in your charger.
- Microphone of the mobile phone
- Vibrator of a mobile phone: Vibrato of a motor for achieving the phone’s vibration feature, when you receive a text message or phone, the motor starts to drive high-speed rotating eccentric done, resulting in vibration.
- Charging connector of a mobile phone
- Headphone connector: A phone connector, also known as phone jack, audio jack, headphone jack or jack plug, is a family of electrical connectors typically used for analog audio signals. The standard is that a plug (described as the male connector) will connect with a jack (described as female).
- Battery of a mobile phone
- SIM Card: A SIM card, or subscriber identity module, is a small card in your cell phone that connects you to the network. Your SIM card contains your phone number, and lets you make phone calls, send text messages, and more.
- SIM card connector
- Memory card of a mobile phone: An memory card, short for Secure Digital card, is a type of removable memory card used to read and write large quantities of data in a wide variety of mobile electronics, including mobile phones.
- Memory card connector
- Camera of a mobile phone: A camera phone is a mobile phone which is able to capture photographs and often record video using one or more built-in digital cameras.
You can see in the Covid lockdowns and our everyday usability of mobile phones has taken a pivotal role. We need mobile phones at every step in our life. Let’s say waking up in the morning with a mobile ringing alarm. Seeing the mails and while taking exercise we counted our steps we walked with the apps of the mobile phone.
Mobile servicing is a crucial need in our economy and this profession has the ability to generate many employments with very low initial cost and time to learn. It is not needed that you have to only do the mobile repairing, you can also import the repairing parts from China or any other country and start a trading business. Apart from the mobile repairing you can keep many mobile accessories like headphones, mobile back covers, chargers and many other things in your small shop that interested customers can buy and you can also import those parts.
This mobile phone repairing sector will grow in the days to come and we have to employ more technicians to take advantage of this sector.
The necessity of the mobile accessories in the market is growing and the new accessories are coming in huge numbers. Apart from very essential mobile phone accessories we have fancy accessories. All this will bring more customers to your mobile repairing shop and increase your business growth.
At present days smart phones are taking the pivotal role in all the steps in our life. We need it and it is essential. So now is the time to learn the mobile repairing or servicing business and develop yourself as a business man in your field and also start importing and expand the business by trading.